CINEMA – Towards circular economy via ecodesignand sustainable remanufacturing
To strengthen the region’s competitiveness and economic growth by increasing entrepreneurship, amount of innovative companies and competitiveness of existing SMEs in the Interreg Nord region.
Branch: Production technology
Duration: 01.06.2018 – 31.12.2021
Region: International
Financed by: European Union Interreg Nord, Lapland Union
Budget: 936 056 EUR
Further information: Markku Hartikainen, +358 40 729 9941, markku.hartikainen@centria.fi
Project Manager: Markku Hartikainen
Funding
Project is funded by Interreg Nord and the total budget is 936 056 EUR.
Interreg V A Nord is a EU-program supporting cross-border cooperation in order to strengthen the economic and social development. Areas included in the program are north Norway, north Finland, north Sweden and Sápmi (which spreads over all three countries).
Project objectives
The main objectives of the project are:
- To strengthen the region’s competitiveness and economic growth by increasing.
entrepreneurship, amount of innovative companies and competitiveness of existing SMEs
in the Interreg Nord region. - To increase SMEs’ cross-border trade, export and internationalisation.
- To develop collaboration between large enterprises and SMEs.
- To promote activities, which support a transition towards the circular economy in the
Interreg Nord region.
These main goals are achieved by fulfilling the sub-goals:
- To bring SMEs and large enterprises together.
- To identify concrete sectors or areas with high potential to support transition to a circular
economy. - To identify the products manufactured in the region, which have a lot of eco-design and
remanufacturing potential. - To develop circular economy business models.
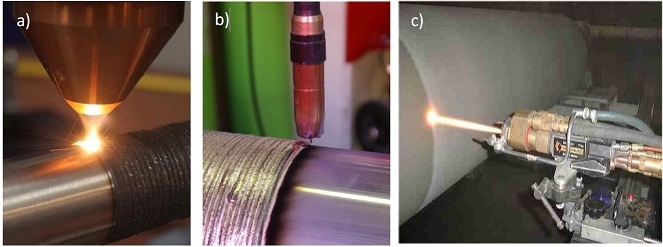
- To identify the possibilities of advanced directed energy deposition technologies in
promotion of remanufacturing and expected environmental benefits - To integrate advanced remanufacturing technologies (LTU: laser-based methods, Centria:
Cold-arc methods, TUT: thermal spraying) in synergic way to offer a service to SMEs and
large enterprises to solve sustainability-oriented problems related to products - To use advanced technologies to restore the product to its original state as well as to
upgrade or add new features to the product, to meet customer needs.
Remanufacturing is an essential part of the concept circular economy. Conventional economic systems used to be based on a linear “takemake – dispose” production model. Products and production were based only on the initial use of the product and recycling is segregated from production. For the circular economy, however, there is a difference between the consumption and use of materials, and the circular economy is based on the sustainable use of resources.
According to the pronciples of circular economy, the circulation of products and raw materials can be promoted in 4 (or 5) ways (Sitra 2014):
1. Maintain: Build products to last longer without repairsand offer maintenance services to prolong product lifecycles enabling longer use by the same owner.
2. Reuse/redistribute: Reuse the product for the same pur-pose on the resale markets.
3. Remanufacture/refurbish: Plan the product life cycle asseveral life cycles and resell the product after thorough-going refurbishment or remanufacture.
4. Recycle: Recycle product materials for reuse and de-sign products so that their materials are easy to sort. For biological materials, it would also be important to con-sider how to ensure the safe and sustainable return of nutrients to the nutrient cycle following their optimal use.
In addition to these four, cascade is often considered to be the fifth way to promote circulation, meanin: Make use of a material or parts of it in another value chain, when it can no longer be used in the original sector.
Remanufacturing is an industrial process by which a used, worn or non-functional product or part is returned to a ‘like-new’ or ‘better-than-new’ condition.
According to one definition stated by the British Standard Institution (BS 8887-2), remanufacturing is an industrial practice of:
“Returning a product to at least its original performance with a warranty that is
equivalent or better than that of the newly manufactured product.”
meaning that warranty given by the remanufacturer is the essential feature that separates remanufacturing from normal repair process.
The scale of the implemention of industrial remanufacturing has been relatively small, but is has a large potential. According to The Finnish Innovation Fund (Sitra) and a conservative scenario, remanufacturing could bring 165–225 million € in additional sales for the Finnish machinery and equipment industry.
Contact
Centria, Finland: Markku Hartikainen, markku.hartikainen@centria.fi, +358 40 729 9941.
TAU, Finland: Jari Tuominen, jari.tuominen@tuni.fi, +358 40 849 0196.
LTU, Sweden: Jesper Sundqvist, jesper.sundqvist@ltu.se, +46 92 049 2596.
Project partners
Centria University of Applied Sciences, Kokkola Finland.
Tampere University, TAU, Tampere Finland.
Lulea University of Technology, LTU, Luleå Sweden.